DENTAL ASIA
Beyond brackets: Rethinking tooth movement with active memory aligners
INTRODUCTION
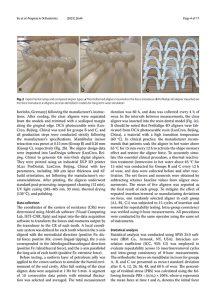
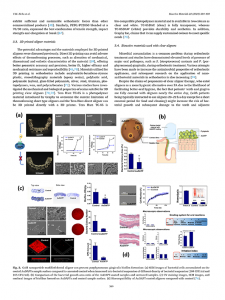
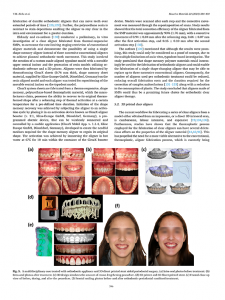
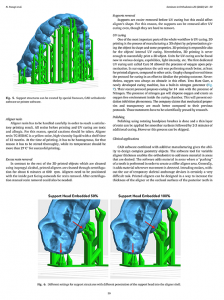
Orthodontic tooth movement is a biologically mediated process in which mechanical forces initiate the remodeling of the periodontal ligament (PDL) and alveolar bone. Contemporary aligner materials, particularly ActiveMemory polymers such as LuxCreo’s Direct Clear Aligner (DCA) and DCA Plus, interact with the viscoelastic properties of the PDL in complex and time-dependent ways. These interactions challenge traditional biomechanical paradigms.
By Dr Jean-Marc Retrouvey
https://dentalasia.net/dental-asia-november-december-2025/
Published: NOVEMBER / DECEMBER 2025
Product Link: https://3dnadental.com/product-category/luxcreo-3d-printers/
Progress in Orthodontics
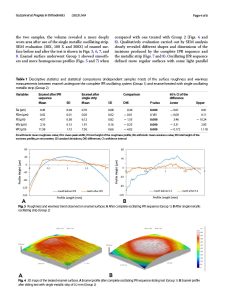
Force comparison between Perfitalign 4D aligners and thermoformed aligners for mandibular incisor retraction: an in vitro study
ABSTRACT
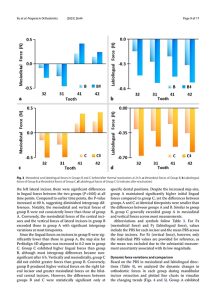
Objectives: To quantitatively compare the orthodontic forces exerted during mandibular incisor retraction by Perfitalign 4D aligners and thermoformed aligners over a 60-hour dynamic monitoring period, assess tooth movement trends, and investigate the effects of shape-memory properties on force characteristics.
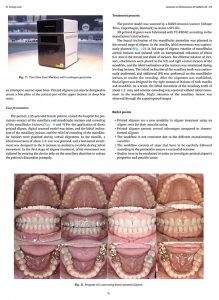
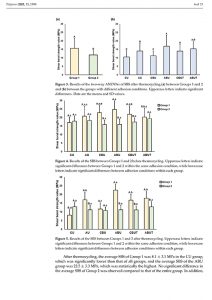
Materials and methods: Three groups of aligners were designed for mandibular incisor retraction. Group A aligners were fabricated using Erkodur foils (ERKODENT Erich Kopp) via thermoforming, while Groups B and C were fabricated using DCA resin (LuxCreo) via 3D printing. Groups A and B possessed a step size of 0.15 mm, whereas group C had a step size of 0.20 mm. Force data were monitored on a mandibular model for 60 h using a multi-axis transducer at 4-hour wear intervals. Groups B and C underwent thermal reactivation after every 12 h of cumulative wear, with recordings taken immediately before and after each activation.
https://tinyurl.com/zmvwsnmj
Published:
Product Link: https://tinyurl.com/5hehkkx8
APOS Trends in Orthodontics
Assessment of active memory of photo-curable resins for LuxCreo DCA direct-printed 3D aligners
ABSTRACT
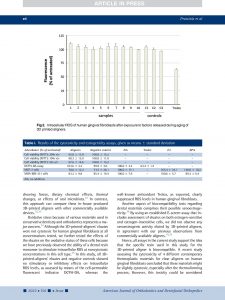
Objectives: Direct 3D-printed aligners represent an innovative advancement in orthodontics, offering a promising alternative to traditional thermoformed aligners. These aligners are fabricated from photo-curable resins with unique shape memory properties, enabling the application of light, continuous forces that optimize tooth movement and treatment efficiency. This study evaluates the thermomechanical properties, shape memory characteristics, and force retention capabilities of two novel photo-curable polymers, direct printed clear aligner (DCA) and DCA Plus, for their suitability in orthodontic applications.
Material and Methods: A series of thermomechanical and mechanical tests were conducted, including dynamic mechanical analysis to assess temperature-dependent modulus changes, shape memory evaluation to measure dimensional stability and recovery, and force restoration tests to quantify sustained orthodontic force application. Statistical analysis, including analysis of variance (P < 0.05), was performed to determine significant differences in material performance.
https://tinyurl.com/mr25ppeb
EPub Ahead of Print: 25 September 2025
Retrouvey J. Assessment of active memory of photo-curable resins for LuxCreo DCA direct-printed 3D aligners. APOS Trends Orthod. doi: 10.25259/APOS_61_2025
Product Link: https://tinyurl.com/5hehkkx8
Heliyon A Cell Press Journal
Prevention of white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets using organoselenium containing antimicrobial enamel surface sealant
ABSTRACT
Objectives: To investigate the antimicrobial potential of organo-selenium compound when applied as enamel surface sealant or primer (DenteShield™ [DS]) around orthodontic brackets to prevent enamel demineralization.
Methods: Human teeth were randomly assigned to seven treatment groups (15/group): control (No primer or sealant), Leopard light primer (LLP), DS Primer (DS-P), DS Enamel Surface Sealant (DS-S), Pro Seal, Opal Seal and combined DS-P/DS-S (DS-PS). Following etching, the tooth surface was coated with their respective material (except control group) and a bracket was bonded on each treated surface. All samples were subject to cariogenic challenge in a continuous flow microbial caries model at 37 C in an incubator for 28 days. Demineralization was evaluated with Transerse microradiography to determine mineral loss (Δz) and lesion depth (LD). Data was statistically analyzed using Bonferroni protected Mann-Whitney tests (α ¼ 0.05).
https://tinyurl.com/mrxa2v46
Published: March 2001
Product Link: https://3dnadental.com/denteshield-and-3dna-dental/
Progress in Orthodontics
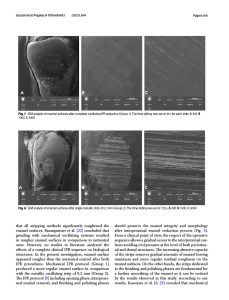
Effects of IPR by mechanical oscillating strips system on biological structures: a quantitative and qualitative evaluation
ABSTRACT
To evaluate by means of profilometric analysis and scanning electronic microscope (SEM) the effects on enamel surfaces of oscillating mechanical systems for interproximal enamel reduction (IPR). Fifteen complete (Group 1) oscillating IPR sequence and 15 single metallic strips (Group 2) for active IPR phase of 0.2 mm were selected and tested on 30 freshly extracted teeth by means of tribological tests with alternative dry-sliding motion (Linear Reciprocating Tribometer, C.S.M. Instruments, Peseaux, Switzerland). Enamel surface roughness and waviness measurements were assessed by contact probe surface profiler (TalySurf CLI 2000; Taylor Hobson, Leicester, UK) and a TayMap software for the 3D analysis. Statistical analysis was performed with independent samples t-test. Significance was established at the P < .05 level. SEM analysis of enamel surfaces was conducted with a FEI Quanta 200 (Hillsboro, USA) in high vacuum at 30.00 kV. Images were acquired at 30X, 100X, and 300X of magnification.
https://tinyurl.com/4js27ny7
Published: Volume 24; 2023
Product Link: https://3dnadental.com/product/dentasonic-ipr-evo-1/
AJO-DO American Journal of Orthodontics & Dentalfacial Orthopedics
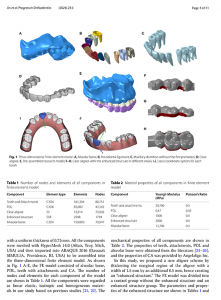
Computer-aided design and manufacture of hyrax devices: Can we really go digital?
ABSTRACT
The aim of this pilot study was to illustrate the feasibility of a new digital procedure to fabricate metallic orthodontic appliances. Hyrax appliances for rapid palatal expansion were produced for 3 patients using a CAD/CAM procedure without physical impressions or printed models. The work flow consisted of intraoral scanning, digital design with incorporation of a scanned prefabricated expansion screw, direct 3-dimensional metal printing via laser melting, welding of an expansion screw, insertion, and finally activation in the patients’ mouths.
https://www.ajodo.org/article/S0889-5406(17)30718-7/fulltext

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=264FQH387fE
Published: December 2017
Product Link: https://3dnadental.com/product/deltaface-customized-appliance-software/
AJO-DO American Journal of Orthodontics & Dentalfacial Orthopedics
Digital orthodontics: Present and future
ABSTRACT
Digital technology has been at the forefront of many innovations in everyday life in recent years. The devel- opment of computer-aided design software, 3-dimensional (3D) printers, surface and volume scanners, and printing resins has had an impact on dentistry and orthodontics. These tools are all already in the arma- mentarium of the orthodontist, enabling the technological advancement of orthodontic appliances, diagno- sis, and treatment…
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666430523001528
Published: February 2024
Progress in Orthodontics
Obstructive sleep apnea: What is an orthodontist’s role?
ABSTRACT
Background: The American Association of Orthodontists white paper on obstructive sleep apnea and orthodontics remains the most authoritative statement on the topic. This was produced in 2019 due to increasing orthodontic interest in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and the lack of formal guidelines for orthodontists. Since the white paper’s release, advocacy for contrarian ideas and practices remain. Orthodontists are sometimes acting as primary care providers for OSA…
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40510-024-00524-4
Published: July 2024
Progress in Orthodontics
The effect of enhanced structure in the posterior segment of clear aligners during anterior retraction: a three‑dimensional finite element and experimental model analysis
ABSTRACT
Background: Mesial tipping of posterior teeth occurs frequently during space closure with clear aligners (CAs). In this study, we proposed a new modification of CA by localized thickening of the aligner to form the enhanced structure and investigate its biomechanical effect during anterior retraction.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40510-023-00502-2
Published: January 2024
Journal of Bioactive Materials
Advances in orthodontic clear aligner materials
ABSTRACT
Rapid technological improvements in biomaterials, computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) have endorsed clear aligner therapy (CAT) as a mainstay of orthodontic treatment, and the materials employed for aligner fabrication play an all-important role in determining the clinical performance of clear aligners. This narrative review has attempted to comprehensively encompass the entire gamut of materials currently used for the fabrication of clear aligners and elucidate their characteristics that are crucial in determining their performance in an oral environment…
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452199X22004303
Published: April 2023
Seminars in Orthodontics
3D Printed Aligners: Material Science, Workflow and Clinical Applications
ABSTRACT
Clear aligner orthodontic treatment is not a new treatment modality. Treatment with the use of plastic invisible removable appliances counts more than 80 years when Kesling introduced the tooth positioner, Sheridan introduced the Essix aligner and Align technology its aligners. In-house designing and aligner fabrication has been around for more than 10 years. The last years a digital technological and material advancement has changed the process of aligner manufacturing from the plastic foil thermoforming procedure to a direct aligner printing one…
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1073874622000809
Published: March 2023
Journal of Polymers
Effect of Adhesion Conditions on the Shear Bond Strength of 3D Printing Resins after Thermocycling Used for Definitive Prosthesis
ABSTRACT
Three-dimensional (3D) printing polymers such as urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA) and ethoxylated bisphenol A dimethacrylate (Bis-EMA) are typically used in definitive prosthesis and require surface treatments before bonding. However, surface treatment and adhesion conditions often affect long-term use. Herein, polymers were divided into Groups 1 and 2 for the UDMA and Bis-EMA components, respectively…
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/15/6/1390
Published: March 2023
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics
Cytotoxicity and estrogenicity of a novel 3-dimensional printed orthodontic aligner
Introduction
Orthodontic aligners printed with in-office 3-dimensional (3D) procedures have been described, but no data on their biocompatibility exist. This study investigates the cytotoxicity and estrogenicity of a 3D-printed orthodontic aligner by assessing its biological and behavioral effects.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/…/pii/S0889540622003961
Published: September 2022
Journal on Children’s Health
Three-Dimensional-Printed Customized Orthodontic and Pedodontic Appliances: A Critical Review of a New Era for Treatment
ABSTRACT
Three-dimensional (3D) designing and manufacturing technology is a direct derivative of digital technology. Three-dimensional volume and surface acquisition, CAD software, and 3D manufacturing are major changes included in daily practice in many orthodontic and pedodontic offices. Customized appliances can be designed using dental CAD software or general-purpose CAD software in the office or a laboratory. Materials that can be used are resins, alloys, or zirconia…
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9067/9/8/1107
Published: July 2022